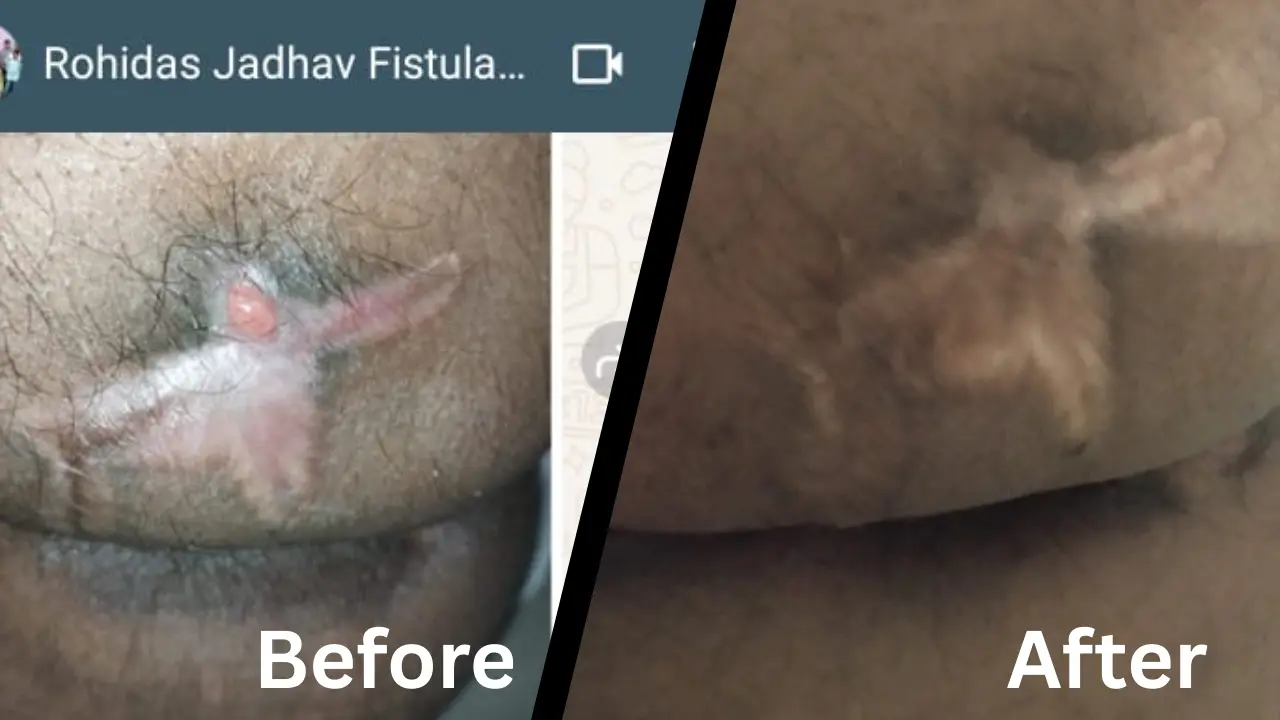
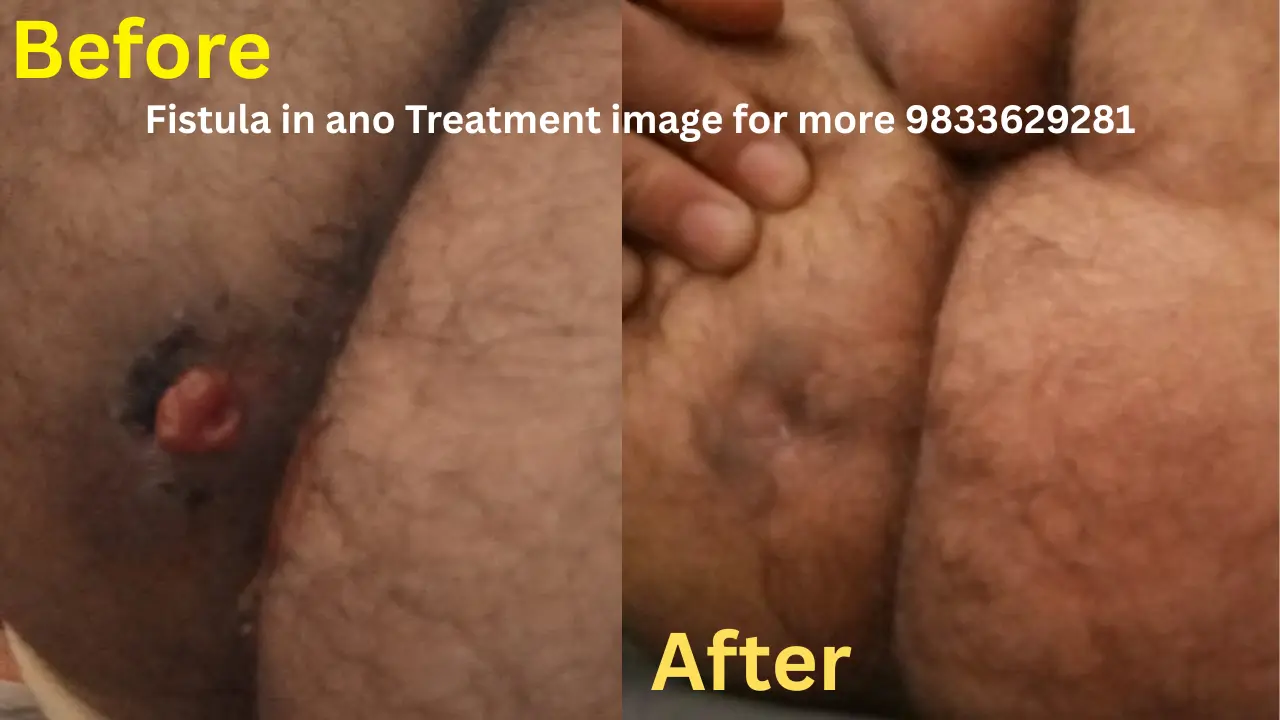
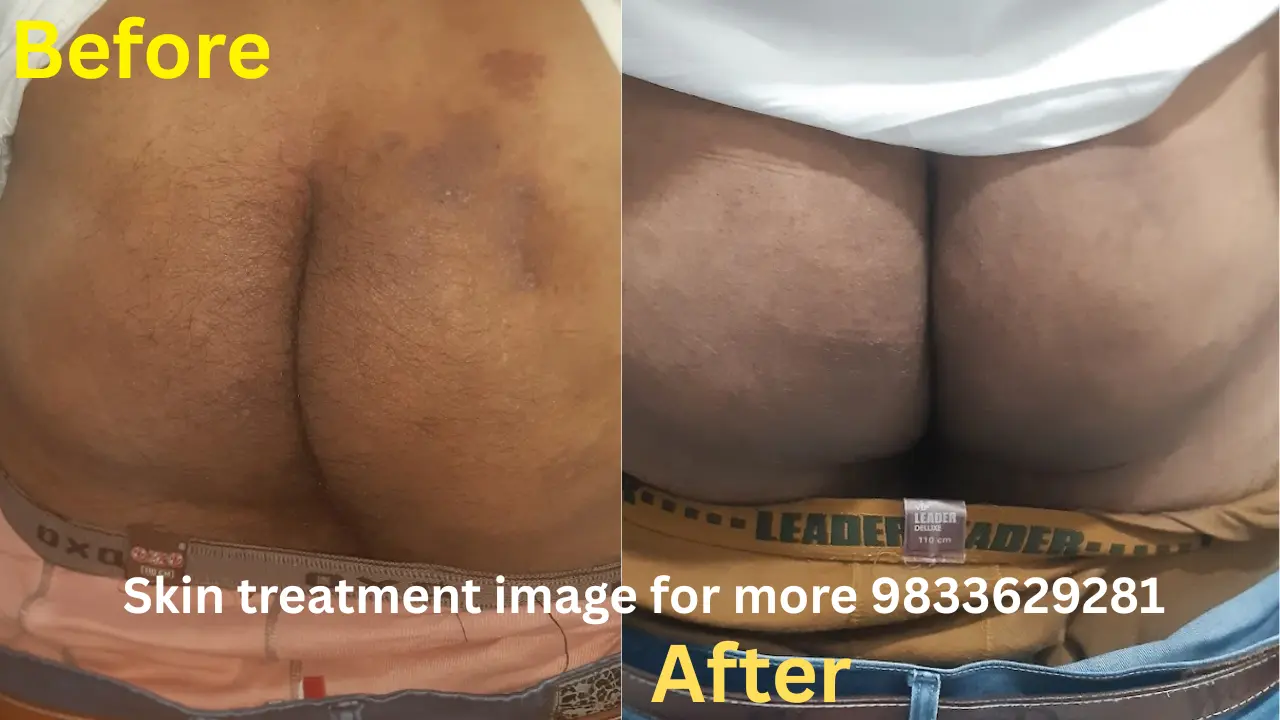
"Shows degenerative osteophytes at the patella and tibia with a prominent tibial spine and decrease in joint space consistent with osteoarthritis"
This is a moderate to advanced case of knee osteoarthritis (OA), particularly affecting the patellofemoral and tibiofemoral joints. Here's how we can understand and approach it:
🩺 Diagnosis Summary
- Degenerative Osteophytes: These are bone spurs caused by the body's attempt to repair cartilage loss.
- Prominent Tibial Spine: May suggest chronic stress or degenerative change.
- Decreased Joint Space: A hallmark of cartilage loss in osteoarthritis.
- Consistent with Osteoarthritis: Confirms diagnosis.
✅ Is Surgery Avoidable?
Yes, surgery may be avoidable — especially in early to moderate stages, depending on:
- Pain level
- Mobility limitation
- Response to non-surgical treatments
- Absence of joint deformity or severe instability
However, if the osteoarthritis is severe (bone-on-bone contact, constant pain at rest, or major restriction in movement), joint replacement might eventually be necessary.
🩹 Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Here’s a complete treatment approach without surgery:
1. Medical Management
-
Homeopathic/Alternative Options (if preferred):
- Rhus Tox 30/200: For stiffness and pain that improves with movement.
- Bryonia 30: For pain worse with movement.
- Calcarea Flour 6X: For bone spurs and degeneration.
-
Symphytum 200: For joint/cartilage repair support.
(Note: Best taken under professional guidance with personalization.)
-
Conventional Supplements:
- Glucosamine + Chondroitin
- Vitamin D3 + Calcium
- Omega-3 fatty acids (fish oil)
2. Diet & Nutrition
-
Anti-inflammatory foods:
- Turmeric, ginger, garlic, berries
- Omega-3-rich foods: walnuts, flaxseeds
-
Avoid:
- Sugary/junk food
- Red meat
- Carbonated drinks
- High salt and processed foods
3. Physiotherapy & Exercise
-
Daily strengthening & flexibility routine:
- Isometric quadriceps exercises
- Straight leg raises
- Hamstring stretches
- Cycling (stationary) or swimming (low-impact exercise)
- Use hot water fermentation or infrared therapy for pain relief.
4. Weight Management
- Even a 5–10% weight reduction can significantly reduce knee stress.
5. Supportive Aids
- Knee braces (unloading type)
- Orthopedic footwear or insoles for alignment
- Walking stick (if needed) on the opposite side of the affected knee
🧠 Lifestyle Tips
- Avoid squatting, stair climbing, and sitting cross-legged
- Use chairs with arm support
- Take breaks during long standing
🧾 Optional: Intra-articular Injections (Non-surgical)
If pain persists:
- Hyaluronic acid injections
-
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections
(These are OPD procedures and not considered surgery)
⚠️ When is Surgery Recommended?
- No relief from the above treatments after 6–12 months
- Severe limitation of daily activities
- Severe joint deformity on X-ray
📌 Final Verdict:
✅ Yes, this condition can be managed without surgery in many cases through:
- Homeopathy or integrative medicine
- Physiotherapy
- Diet and lifestyle modification
Would you like me to prepare a personalized non-surgical plan, printable treatment chart, or homeopathic prescription chart with dosages and duration?